Cormit well/aquifer analytics
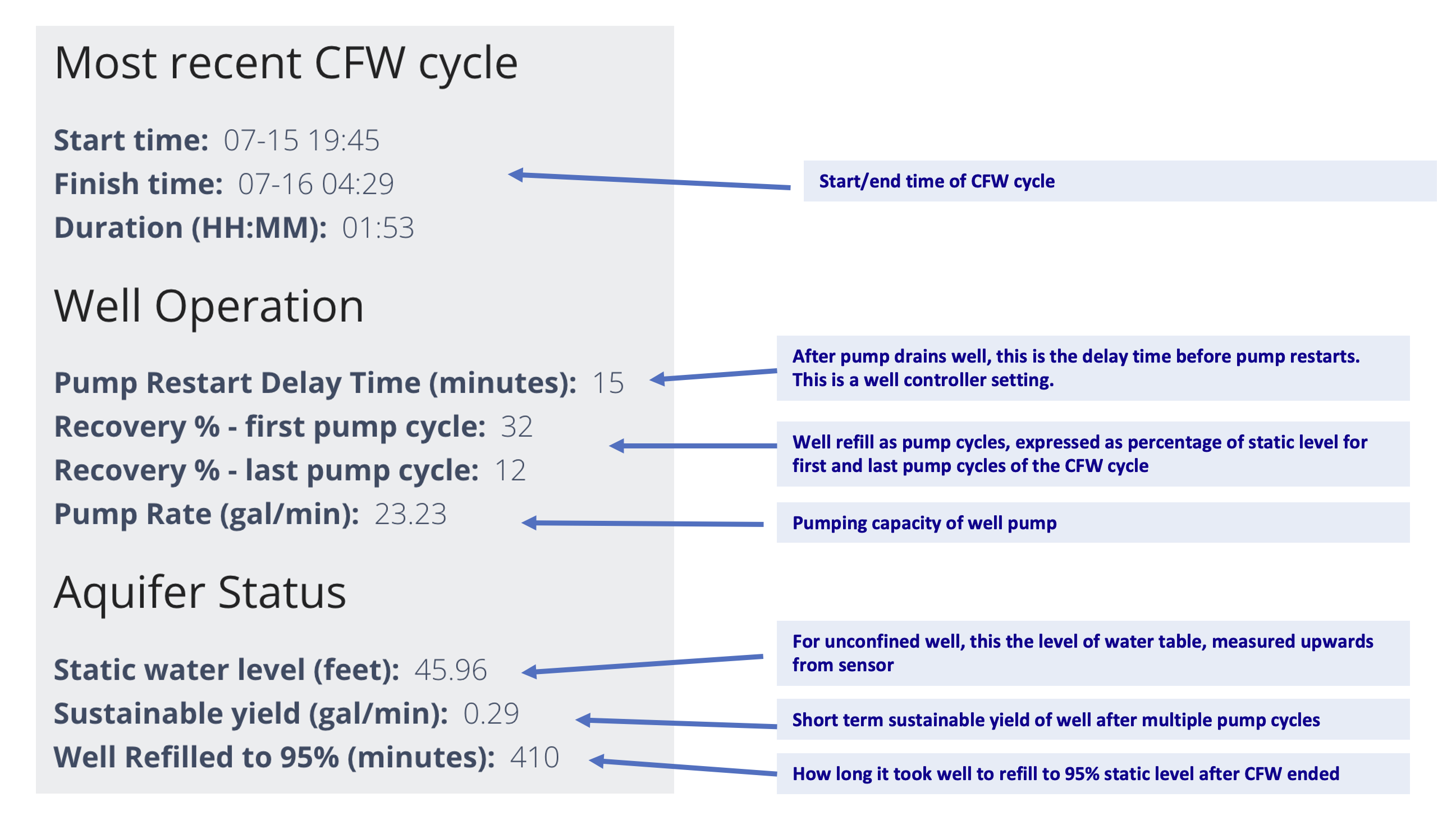
Summary metrics—latest CFW cycle
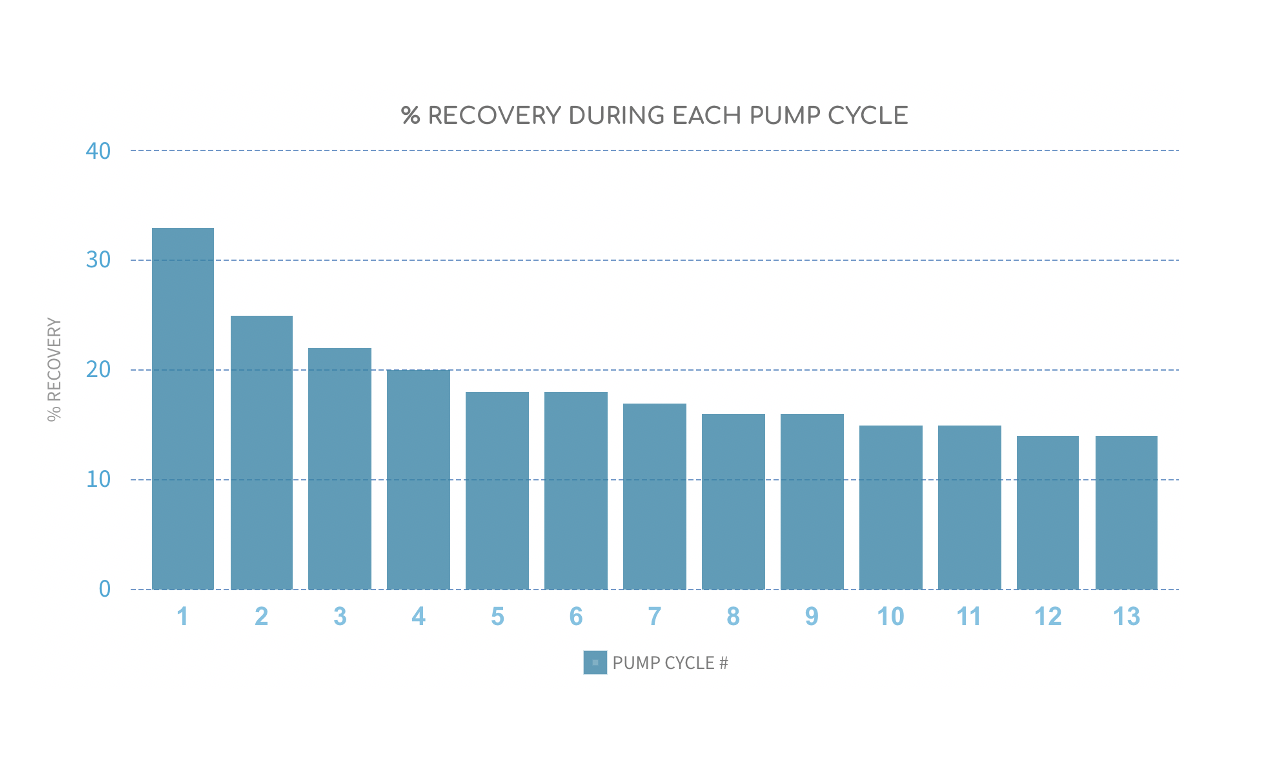
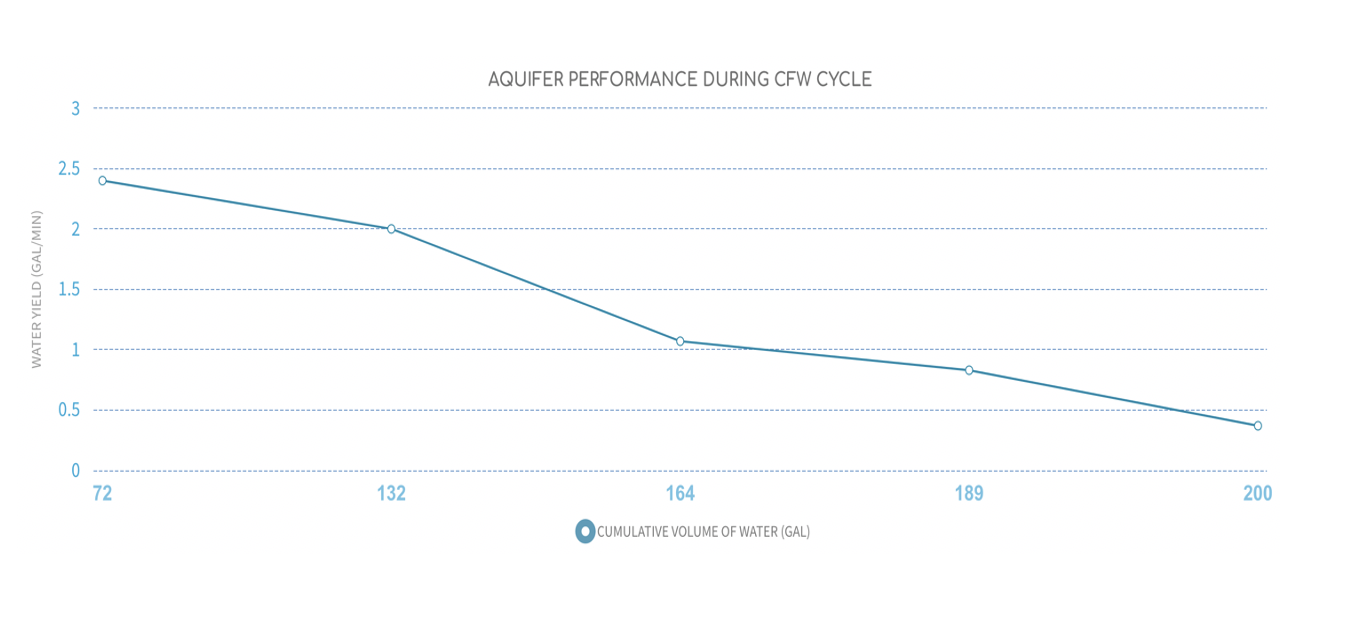
Aquifer performance—pump cycling during CFW
% recovery for each pump cycle: Amount the well refills during each pump cycle as the pump starts and stops during a CFW. The refill is expressed as a percentage of the static water level (% recovery). Generally, the aquifer’s ability to deliver water to the pump declines initially and then stabilizes if the CFW cycle progresses long enough.
Water yield over CFW cycle: Well output (in gallons/min) as function of cumulative volume of water pumped during a CFW cycle. Generally, the well output drops and then reaches equilibrium level as pumping continues. The water yield (gallons per minute) after well output stabilizes is the sustainable yield of the well/aquifer system.
Aquifer performance—refilling well after CFW
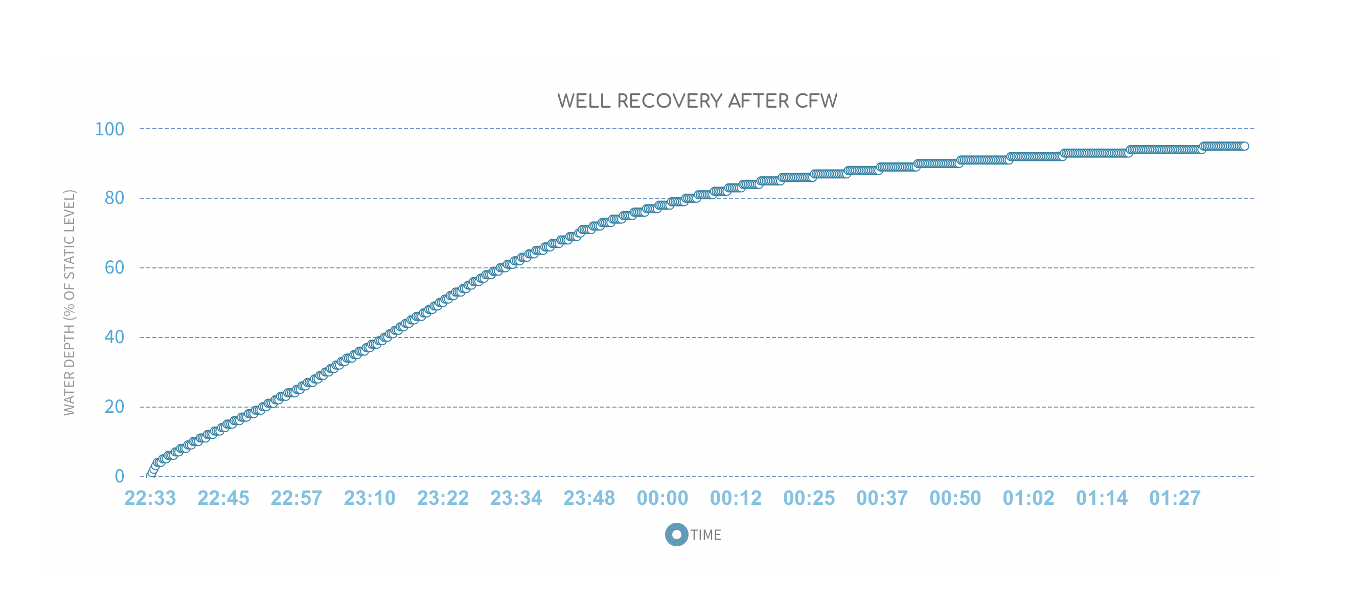
Refill after CFW: This graph shows the well refilling after a CFW cycle ends as a function of time after CFW ends. The refill is measured as the height of water in the well, expressed as a percentage of the static water level (measured immediately before the CFW cycle).
If the refill curve starts out linear (straight line), it means the bottom of the aquifer is above the level of the depth sensor in the well.
The point at which the initial linear segment ends and rate of refill slows marks the bottom of the aquifer.
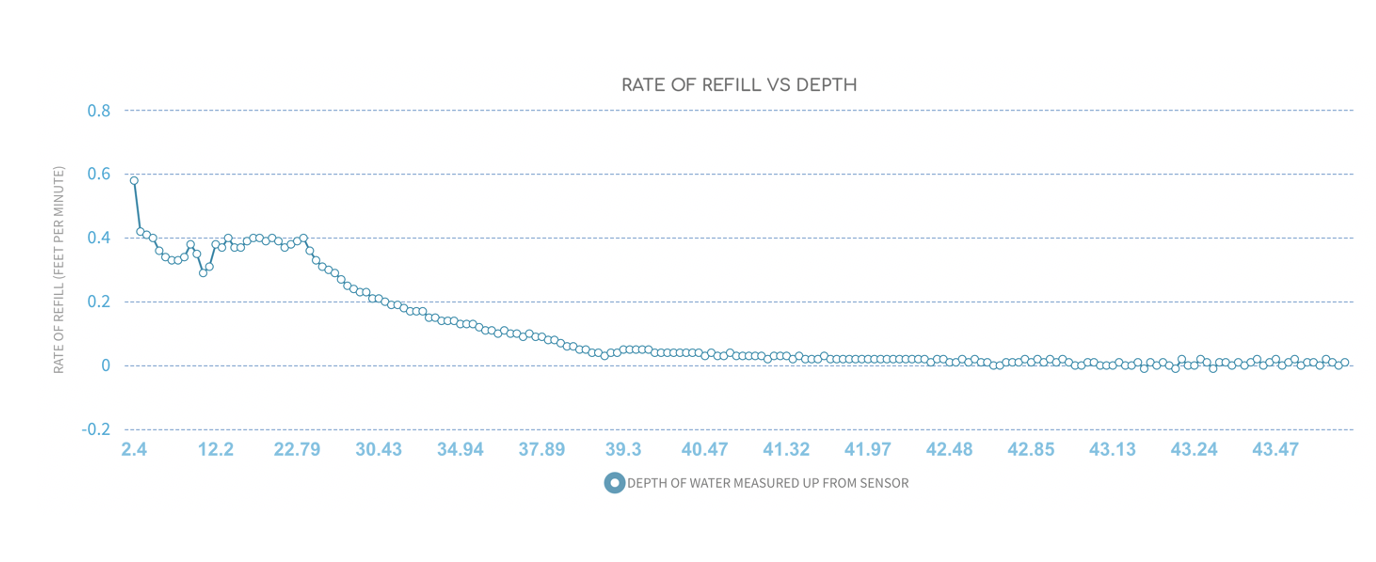
Rate of refill as function of depth: This graph shows the rate at which the well is refilling after a CFW cycle ends as a function of the depth of water in the well.
The rate of refill is measured in inches (of the depth of water in the well). Initially, the rate will be high as the entire well is empty and there is no hydrostatic pressure in the well pushing back against water trying to enter the well.
As the well fills with water and the depth goes above the bottom of the aquifer, hydrostatic pressure of the water in the well slows the rate of refill.
Monitoring well—water yield and water depth in well
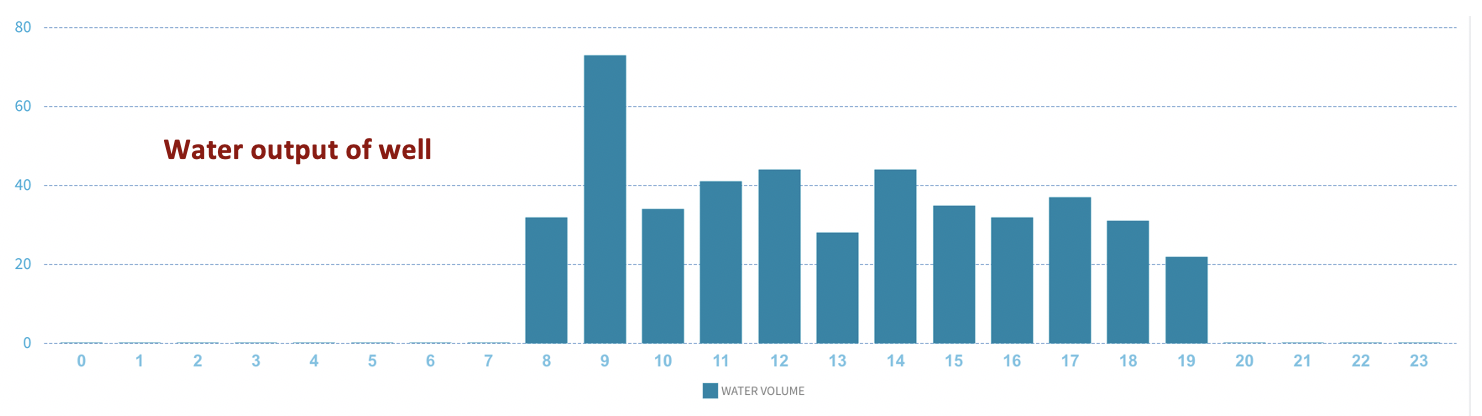
Well output: Single day graph showing water pumped out of well. CFW is initiated during hour 8 and ends during hour 19.
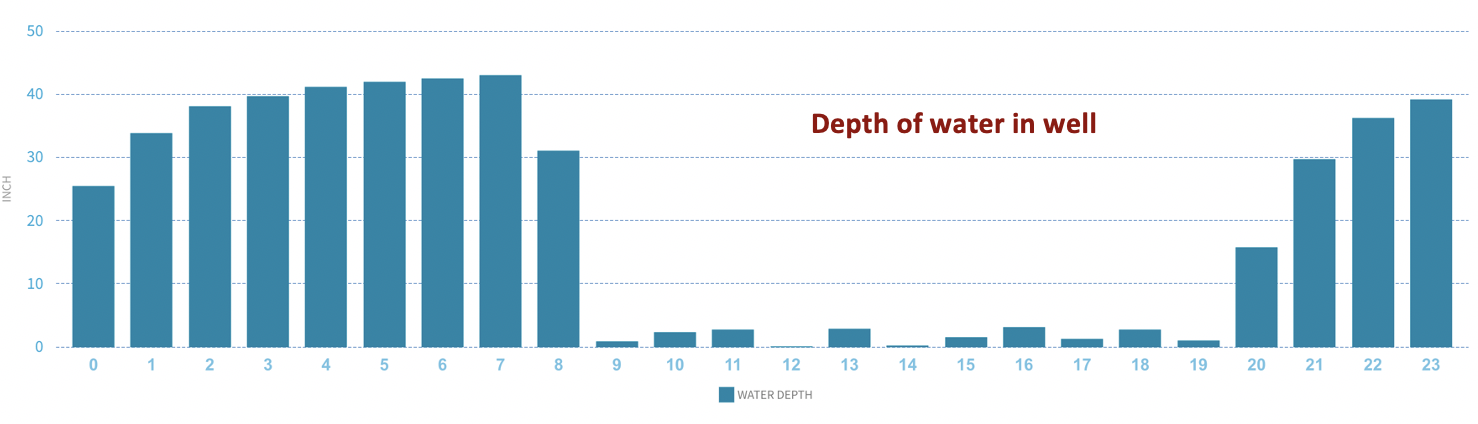
Water depth in well: Single day graph. Prior to CFW initiated during hour 8, well is refilling and depth reaches static water level. During CFW, depth of water remains low as the the well does not refill very much during pump cycling.
Long-term trends
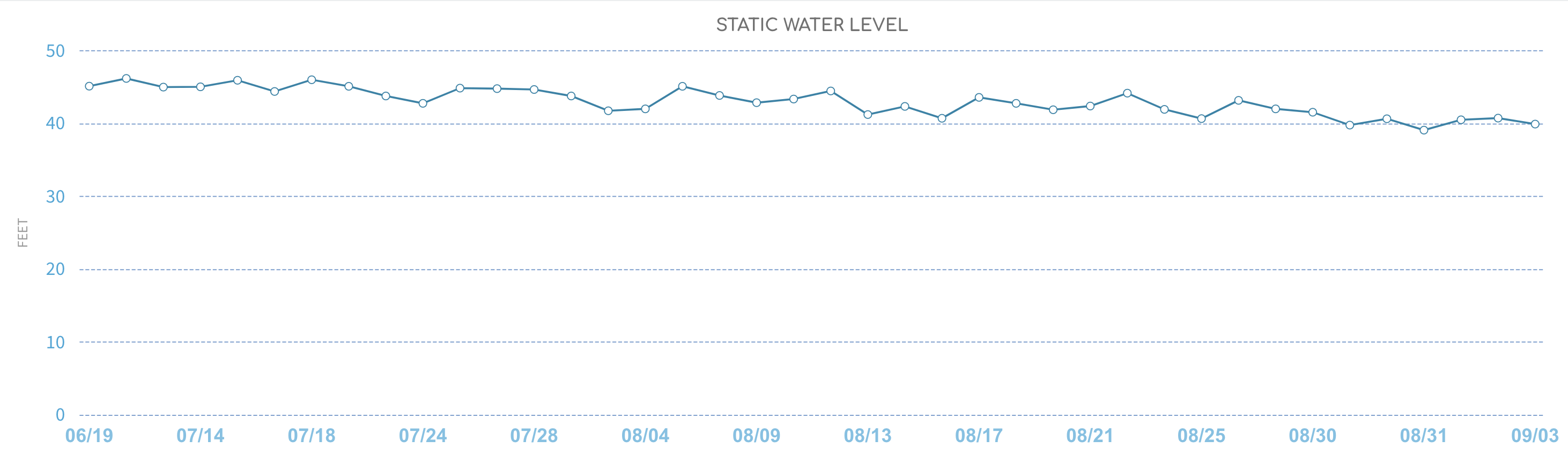
- Static water level
- Sustainable yield
- Well recovery to 95% static level
- CFW duration
- Restart delay
- % recovery—first/last pump cycle
- Pump rate (GPM)